Hold down the T key for 3 seconds to activate the audio accessibility mode, at which point you can click the K key to pause and resume audio. Useful for the Check Your Understanding and See Answers.
 Refraction is the bending of the path of a light wave as it passes from one material to another material. The refraction occurs at the boundary and is caused by a change in the speed of the light wave upon crossing the boundary. The tendency of a ray of light to bend one direction or another is dependent upon whether the light wave speeds up or slows down upon crossing the boundary. Because a major focus of our study will be upon the direction of bending, it will be important to understand the factors that affect the speed at which a light wave is transported through a medium.
Refraction is the bending of the path of a light wave as it passes from one material to another material. The refraction occurs at the boundary and is caused by a change in the speed of the light wave upon crossing the boundary. The tendency of a ray of light to bend one direction or another is dependent upon whether the light wave speeds up or slows down upon crossing the boundary. Because a major focus of our study will be upon the direction of bending, it will be important to understand the factors that affect the speed at which a light wave is transported through a medium.
Light Propagation Through a Medium
The mechanism by which a light wave is transported through a medium occurs in a manner that is similar to the way that any other wave is transported - by particle-to-particle interaction. In Unit 10 of The Physics Classroom Tutorial, the particle-to-particle interaction mechanism by which a mechanical wave transports energy was discussed in detail. In Unit 12 of The Physics Classroom Tutorial, the mechanism of energy transport by an electromagnetic wave was briefly discussed. Here we will look at this method in more detail.
An electromagnetic wave (i.e., a light wave) is produced by a vibrating electric charge. As the wave moves through the vacuum of empty space, it travels at a speed of c (3 x 108 m/s). This value is the speed of light in a vacuum. When the wave impinges upon a particle of matter, the energy is absorbed and sets electrons within the atoms into vibrational motion. If the frequency of the electromagnetic wave does not match the resonant frequency of vibration of the electron, then the energy is reemitted in the form of an electromagnetic wave. This new electromagnetic wave has the same frequency as the original wave and it too will travel at a speed of c through the empty space between atoms. The newly emitted light wave continues to move through the interatomic space until it impinges upon a neighboring particle. The energy is absorbed by this new particle and sets the electrons of its atoms into vibration motion. And once more, if there is no match between the frequency of the electromagnetic wave and the resonant frequency of the electron, the energy is reemitted in the form of a new electromagnetic wave. The cycle of absorption and reemission continues as the energy is transported from particle to particle through the bulk of a medium. Every photon (bundle of electromagnetic energy) travels between the interatomic void at a speed of c; yet time delay involved in the process of being absorbed and reemitted by the atoms of the material lowers the net speed of transport from one end of the medium to the other. Subsequently, the net speed of an electromagnetic wave in any medium is somewhat less than its speed in a vacuum - c (3 x 108 m/s).

Optical Density and the Index of Refraction
Like any wave, the speed of a light wave is dependent upon the properties of the medium. In the case of an electromagnetic wave, the speed of the wave depends upon the optical density of that material. The optical density of a medium is not the same as its physical density. The physical density of a material refers to the mass/volume ratio. The optical density of a material relates to the sluggish tendency of the atoms of a material to maintain the absorbed energy of an electromagnetic wave in the form of vibrating electrons before reemitting it as a new electromagnetic disturbance. The more optically dense that a material is, the slower that a wave will move through the material.
One indicator of the optical density of a material is the index of refraction value of the material. Index of refraction values (represented by the symbol n) are numerical index values that are expressed relative to the speed of light in a vacuum. The index of refraction value of a material is a number that indicates the number of times slower that a light wave would be in that material than it is in a vacuum. A vacuum is given an n value of 1.0000. The n values of other materials are found from the following equation:
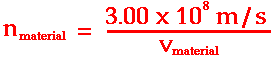
The table below lists index of refraction values for a variety of medium. The materials listed at the top of the table are those through which light travels fastest; these are the least optically dense materials. The materials listed at the bottom of the table are those through which light travels slowest; these are the most optically dense materials. So as the index of refraction value increases, the optical density increases, and the speed of light in that material decreases.
|
Material
|
Index of Refraction
|
|
|
Vacuum
|
1.0000
|
<--lowest optical density
|
|
Air
|
1.0003
|
|
|
Ice
|
1.31
|
|
|
Water
|
1.333
|
|
|
Ethyl Alcohol
|
1.36
|
|
|
Plexiglas
|
1.51
|
|
|
Crown Glass
|
1.52
|
|
|
Light Flint Glass
|
1.58
|
|
|
Dense Flint Glass
|
1.66
|
|
|
Zircon
|
1.923
|
|
|
Diamond
|
2.417
|
|
|
Rutile
|
2.907
|
|
|
Gallium phosphide
|
3.50
|
<--highest optical density
|
Look it Up!
Use the Index of Refraction widget to look up the index of refraction of a given material. Type the name of the material and click the Submit button to find its index of refraction.
The index of refraction values provide a measure of the relative speed of a light wave in a particular medium. Knowledge of such relative speeds allows a student of physics to predict which way a light ray would bend when passing from one medium to another. In the next part of Lesson 1, the rules for the direction of bending will be discussed in detail.
We Would Like to Suggest ...

Why just read about it and when you could be interacting with it? Interact - that's exactly what you do when you use one of The Physics Classroom's Interactives. We would like to suggest that you combine the reading of this page with the use of our
Refraction Interactive or our
Least Time Principle Interactive. You can find these in the Physics Interactives section of our website. These Interactives provide the learner an interactive enivronment for exploring the refraction and/or reflection of light at a boundary between two materials.